
Generative AI Proficiency and Responsible Usage
This interactive module is specifically designed to demystify Generative Artificial Intelligence and build AI Proficiency across the organization.
Developed in close collaboration with our AI experts, this program focuses on awareness, practical application, and establishing core competencies for the responsible use of AI tools.
Module Objectives:
Build AI Literacy: Grasp key concepts, limitations, and the ethical and security challenges specific to our industry.
Master AI Proficiency: Acquire robust techniques for formulating effective inputs and apply AI tools safely and efficiently in a corporate environment.
Develop Applied Competency: Identify AI application opportunities within daily tasks and business processes.
| Responsable | Geoffrey ROMAN JIMENEZ |
|---|---|
| Dernière mise à jour | 12/11/2025 |
| Temps d'achèvement | 4 heures 7 minutes |
| Membres | 3 |

Welcome
General Introduction: Understanding the AI Fundamentals
Voir tout
History of AI: The Cycles of Evolution
The history of AI is not a straight line; it's a result of technological cycles and human ambition.
Turing Test
Mathematician Alan Turing proposed the famous test: "Can a machine converse so naturally that a human can't tell it's a computer?" This set the ultimate goal for the field.
Official Birth of AI

The field is officially recognized at the Dartmouth Conference
The 1st Artificial Neuron
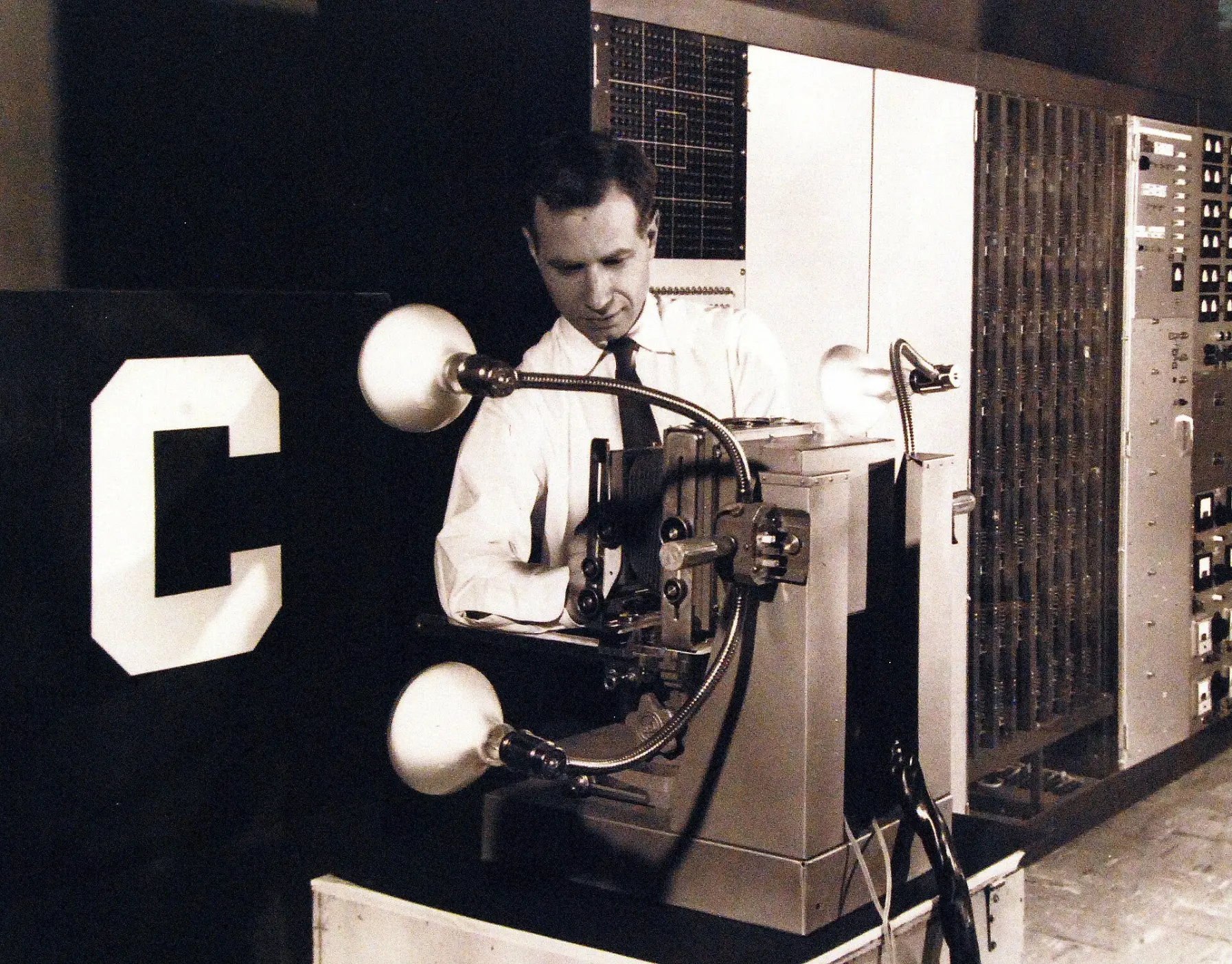
Researchers established the mathematical model for the artificial neuron. This tiny digital unit is the fundamental building block for all modern AI systems
First Signs of Conversation (ELIZA)

Researchers created early programs like ELIZA that could convincingly simulate a conversation, fueling major excitement.
The First "AI Winter"
Enthusiasm fades. Computers of the era were too slow and lacked the memory to handle the complex models researchers dreamed of.
The 2nd "AI Winter"
Expert Systems proved too costly to maintain and too rigid. They required human experts to constantly update their vast database of rules, making them inflexible and expensive to adapt to new information. This caused a new pause in funding.
IBM Deep Blue vs Human
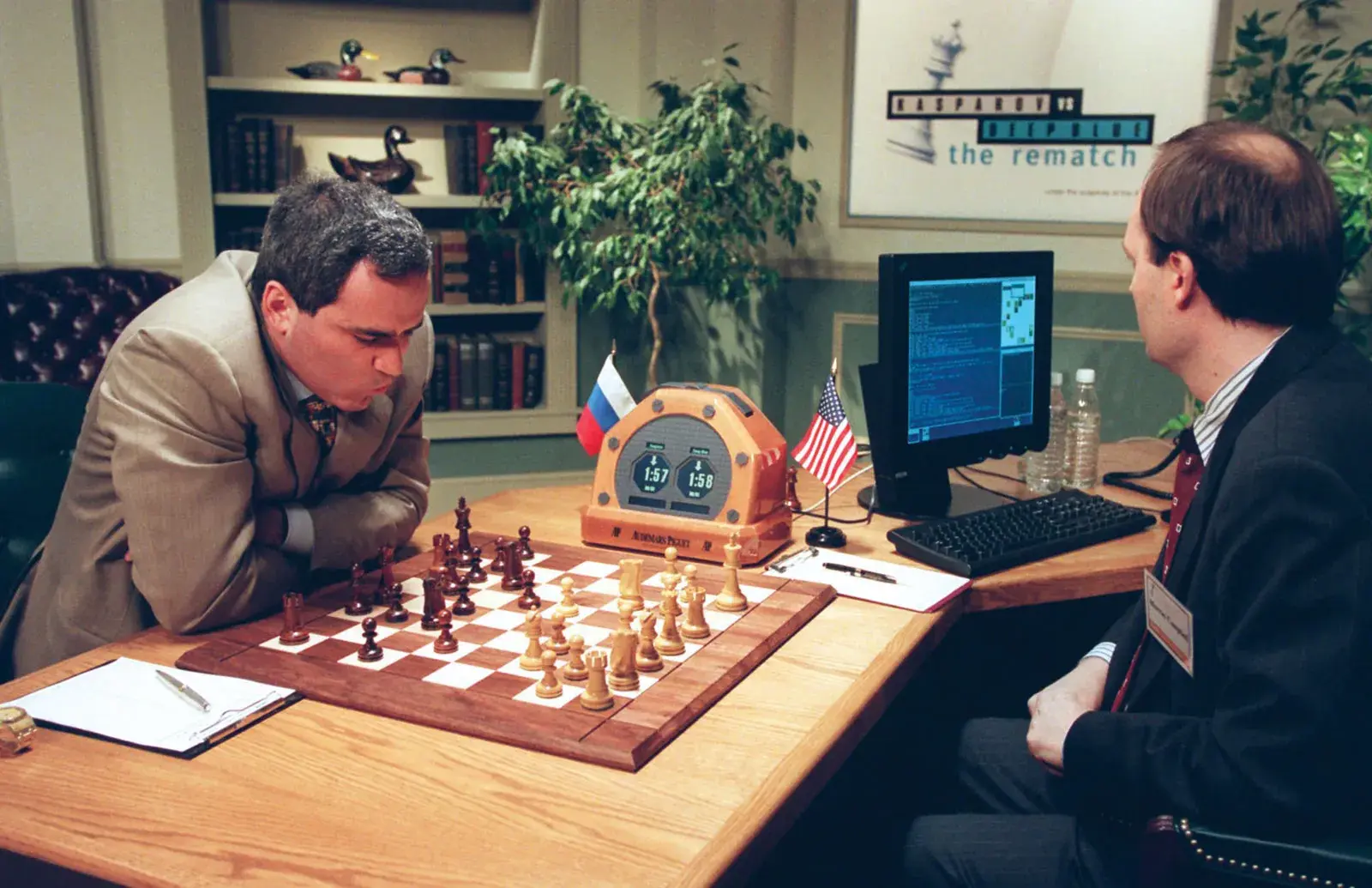

The victory of IBM Deep Blue over the world chess champion (Gary Kasparov) showed the incredible power of highly specialized, rules-driven systems in a controlled, limited environment like chess. This success was a symbolic moment, but it didn't solve the core problems of real-world AI applications.
Success of Expert Systems

AI finds commercial success in very specific fields (like medical diagnosis) using Expert Systems based on thousands of rules coded by humans.
The 1st Artificial Neuron
Researchers established the mathematical model for the artificial neuron. This tiny digital unit is the fundamental building block for all modern AI systems
Turing Test
Mathematician Alan Turing proposed the famous test: "Can a machine converse so naturally that a human can't tell it's a computer?" This set the ultimate goal for the field.